In the realm of property construction, the concept of "right to light" plays a significant role in ensuring that existing properties can enjoy sufficient natural light. As additional info continue to grow and densify, grasping the consequences of right to light becomes critical for developers, architects, and homeowners alike. A right to light survey serves as a important tool in this process, providing insights into how new developments may affect the illumination status of surrounding buildings.
This article examines the principles behind right to light calculations, exploring what constitutes a right to light survey and its role within the planning and development framework. From legislative guidelines to real-world implications, we will highlight why right to light matters in property development and how it can influence building permits and planning decisions. Whether you are starting a new build or planning an extension, understanding when to commission a right to light survey can help reduce possible conflicts and promote harmonious relationships with neighbors.
Understanding Light Rights
The right to light is a juridical entitlement that allows property owners to enjoy unobstructed natural light in their structures. This right is established in the common law system and protects light that has been enjoyed for a specific period, usually two decades. If a recent development obstructs this light, the impacted property owner may have the grounds for a legal claim. Comprehending the nuances of this right is essential, especially for developers who seek to navigate potential disputes and guarantee adherence with lawful standards.
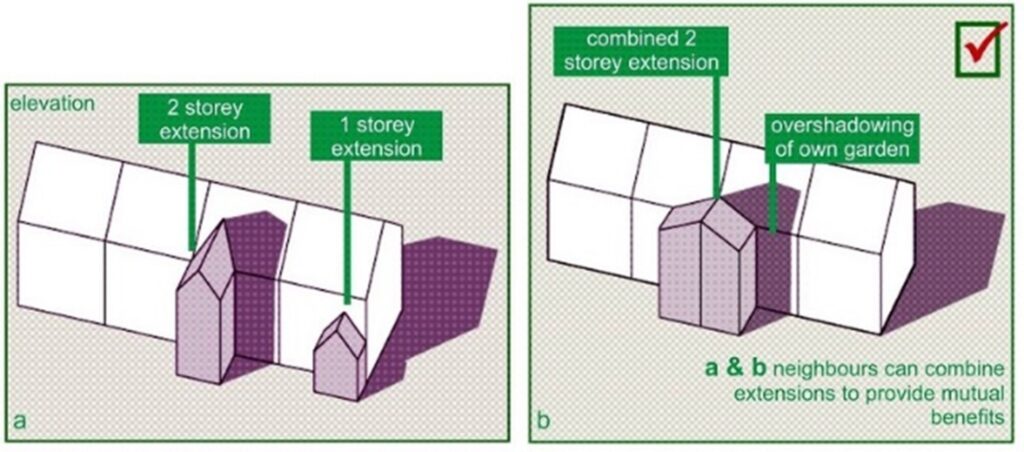
In the context of property development, right to light surveys evaluate how new constructions might affect the light received by neighboring properties. These surveys utilize various instruments and techniques, including 3D modeling, daylight analysis, and adherence to UK standard guidelines. The findings provide developers with insights into whether their proposals could violate the light rights of neighboring properties, allowing them to make informed decisions and modifications to their projects.
Additionally, the importance of right to light goes beyond mere light access; it plays a critical role in the planning and development process. With growing urban density, conflicts over light rights are becoming more common, necessitating a forward-thinking approach to assess and evaluate potential impacts. By recognizing and respecting right to light issues, developers can lessen risks, avoid costly legal disputes, and foster positive relationships with adjacent property owners.
Legal Considerations and Conformity
Grasping the legal framework surrounding light entitlements is important for both property developers and property owners. In the UK, the legal right to light is grounded through the Prescription Act of 1832, which permits individuals to claim a right to light after 20 years of uninterrupted use. This makes it essential for developers to consider existing light rights in their planning processes to avoid potential lawsuits. Omission to recognize these rights can result in financial disputes and setbacks.
Compliance with planning regulations is a further important consideration of right to light matters. Developers must strike a balance between their projects and the rights of adjacent properties, making sure that their plans do not violate light access for nearby structures. Starting in early conversations with municipal authorities and conducting thorough right to light surveys will help developers grasp any limitations or criteria that may be mandated during the planning permission process.
Moreover, judicial remedies for right to light violations can differ, and grasping these options is important for developers. Injunctions may be sought to stop construction that would obstruct light, and in some cases, damages may be offered to impacted residents. It is recommended to involve legal experts at the outset in the project to manage these complexities efficiently and reduce the risk of disputes that could threaten development timelines and budgets.
Examination Process and Methods
The procedure of conducting a Right to Light survey begins with a detailed site assessment. Surveyors examine the existing state of the property and its surroundings, gauging the height of buildings, distances among structures, and the orientation of neighboring properties. This data is essential for understanding how much light a property currently receives and will persist to receive in the times ahead. Evaluators often use exact measurement tools and techniques, such as leveling instruments and total stations, to ensure accuracy in their calculations.
Once the initial assessment is concluded, the next step entails a detailed analysis using tailored software. This often includes creating 3D models of the buildings in question, which allows assessors to simulate light penetration under multiple scenarios. Employing software conforming with the BRE helps to evaluate daylight and sunlight access, ensuring that all assessments adhere to industry standards. The integration of on-site measurements and sophisticated modeling techniques provides a strong framework for evaluating potential infringements on light rights.
Finally, evaluators compile their findings into a thorough report that outlines the implications for property development. This report includes thorough visuals, such as shadow studies and light availability charts, which depict the impact of proposed developments on both the subject property and adjoining sites. By clearly presenting this information, developers can make educated decisions that seek to lessen conflicts and comply with legal requirements surrounding light rights, ultimately contributing to successful project outcomes.